Computer-Aided Design
A core goal of my research is to inject some creativity on the part of the computer and become an artificial designer contributing its own ideas and providing feedback and advice similarly to a colleague of the human designer.
Consistent Game Content Creation via Function Calling for Large Language Models
Roberto Gallotta, Antonios Liapis, Georgios N. Yannakakis
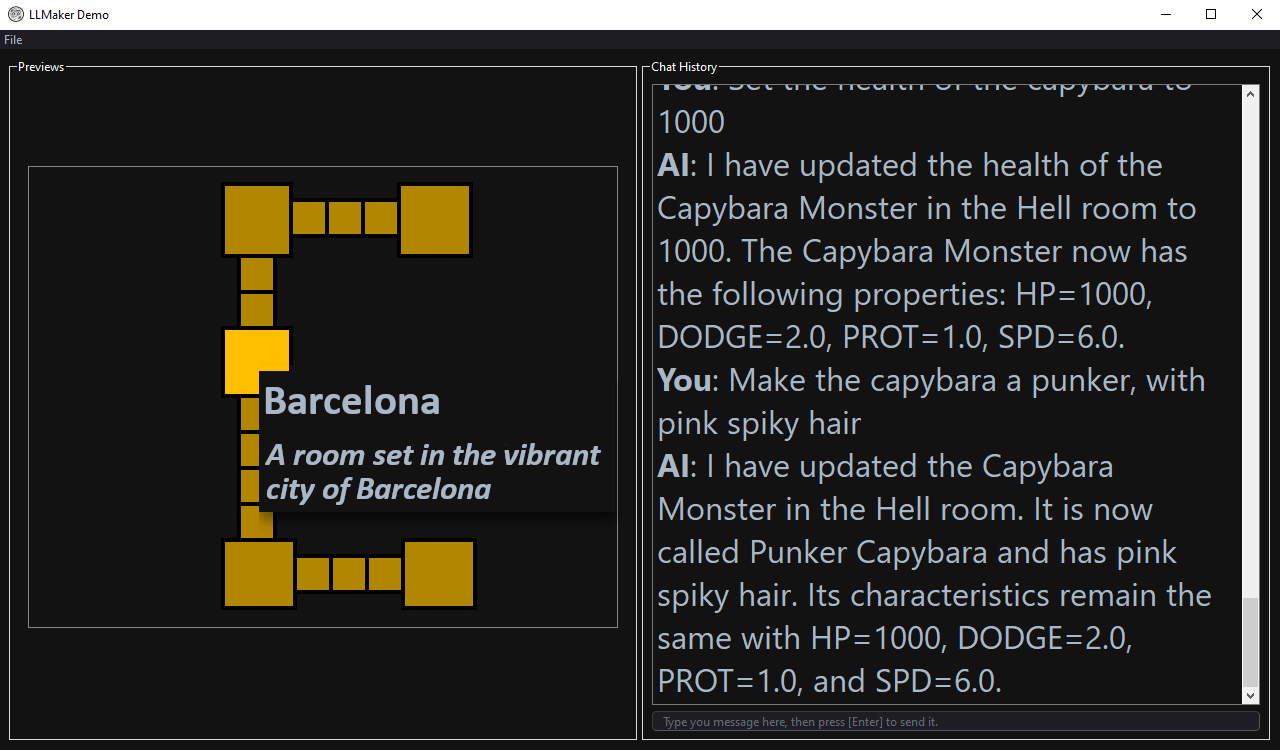
Chat-based interface with room layout (left pane) and natural language dialogue between designer and LLM (right pane).
Abstract: Tools for designing content require a medium that allows the designer to efficiently express their creativity, and a system that ensures the content being designed adheres to the domain of interest. Interacting with Large Language Models (LLMs) via natural language is extremely intuitive for a human designer, although it remains largely unexplored. However, this approach has a limitation: LLMs are prone to hallucinations and they tend to ignore parts of the user request in their responses. One workaround is to let LLM use tools such as function calling to ensure consistency of the content. We formalise this approach by proposing LLMaker, a general framework for consistent video game content generation empowered by LLMs, bridging the gap between creative vision and technical execution. We demonstrate LLMaker's application in generating dungeon crawler level layouts, comparing it against alternative LLM-based methods for content generation over multiple tests, testing for consistency of the outputs and elapsed time per request.
in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Games, 2024. BibTex
LLMaker: A Game Level Design Interface Using (Only) Natural Language
Roberto Gallotta, Antonios Liapis, Georgios N. Yannakakis
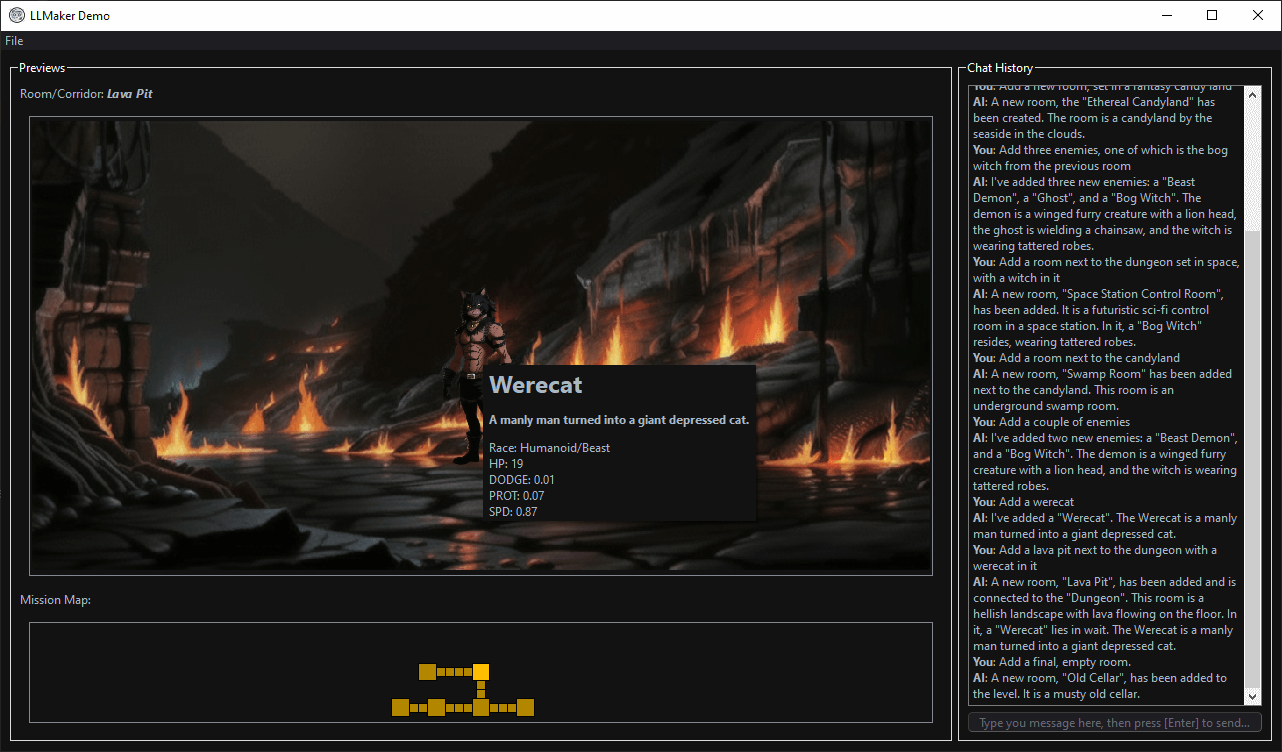
A screenshot of the LLMaker chat-based level design interface. On the upper left pane, the preview of the currently selected room. On the lower left pane, the generated level layout, with rooms (larger squares) and corridors (smaller squares). On the right pane, the chat area with the conversation between designer and LLM.
Abstract: In this demo paper we present LLMaker, a video-game level design tool that operates solely via natural language instructions. Unlike existing level design tools, LLMaker allows the designer to express their intent in an intuitive way, interacting with a cognitively undemanding interface, while still ensuring the generated levels adhere to specific domain and playability constraints.
in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Games, 2024. BibTex
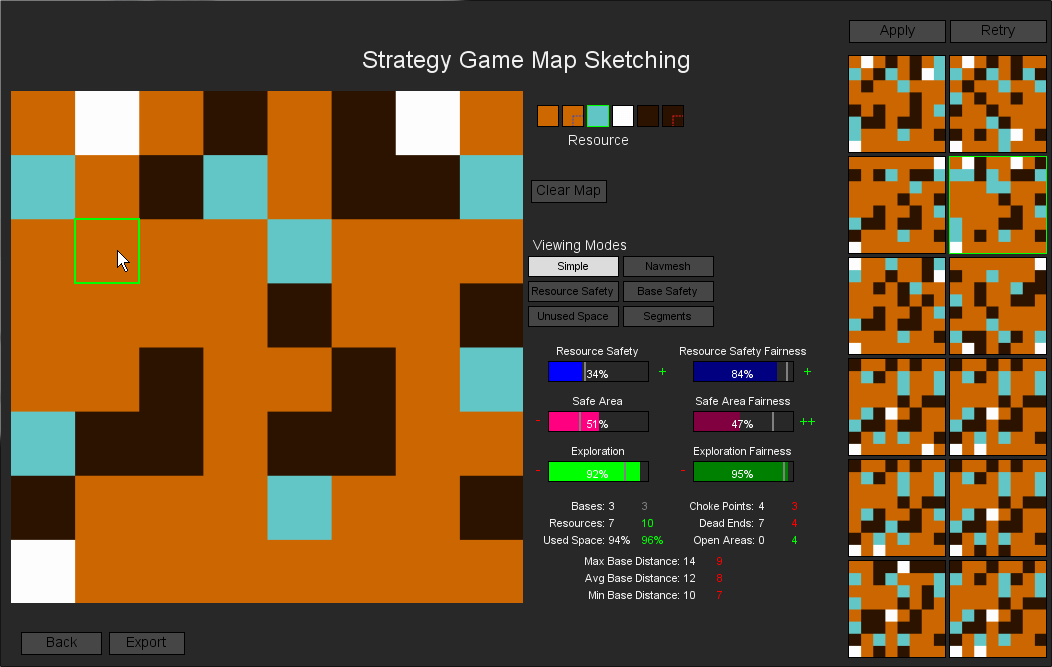
Controllable Exploration of a Design Space via Interactive Quality Diversity
Konstantinos Sfikas, Antonios Liapis and Georgios N. Yannakakis
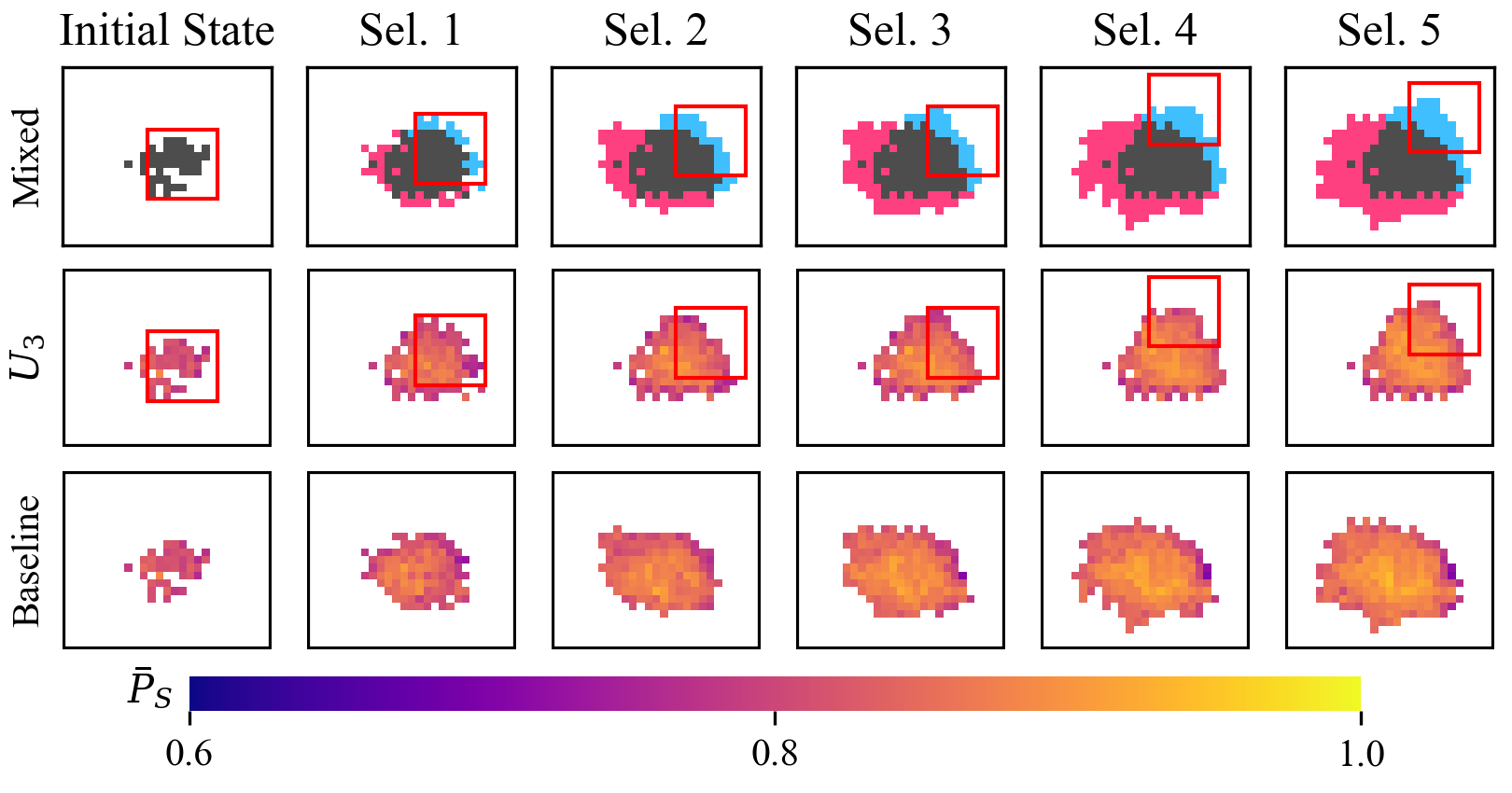
Behavioral space exploration for the baseline MAP-Elites (bottom row) and UC-ME, for the first 5 user selections. Their shared color scale (bottom) is the feasible quality. The top row shows coverage differences: red cells are discovered only by the baseline, blue cells are discovered only by UC-ME and gray cells are common.
Abstract: This paper introduces a user-driven evolutionary algorithm based on Quality Diversity (QD) search. During a design session, the user iteratively selects among presented alternatives and their selections affect the upcoming results. We implement a variation of the MAP-Elites algorithm where the presented alternatives are sampled from a small region (window) of the behavioral space. After a user selection, the window is centered on the selected individual's behavior characterization, evolution selects parents from within this window to produce offspring, and new alternatives are sampled. Essentially we define an adaptive system of local QD search, where the user's selections guide the search towards specific regions of the behavioral space. The system is tested on the generation of architectural layouts, a constrained optimization task, leveraging QD search through a two-archive approach.
in Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference Companion, 2023. BibTex
Designing for Playfulness in Human-AI Authoring Tools
Antonios Liapis, Christian Guckelsberger, Jichen Zhu, Casper Harteveld, Simone Kriglstein, Alena Denisova, Jeremy Gow and Mike Preuss
Abstract: Many human-AI authoring tools are used in a playful way, while being primarily designed for task-achievement -- not playfulness. We argue that playfulness is an important yet overlooked factor of user behaviour and experience when interacting with such tools. Motivating and rewarding playfulness as an exploratory, task-agnostic, open, and subversive attitude can support the satisfaction of more diverse user goals, and have a strong, positive effect on the user experience, the emerging human-AI interaction, and the resulting artefact. In this paper, we motivate the importance of playfulness as user experience in human-AI authoring tools, and propose concrete strategies to design for playfulness in the human user through UI design, in the AI through algorithms, or through interventions to their dialog. We conclude with an outlook of the research agenda.
in Proceedings of the FDG workshop on Human-AI Interaction Through Play, 2023. BibTex
SuSketch: Surrogate Models of Gameplay as a Design Assistant
Panagiotis Migkotzidis and Antonios Liapis
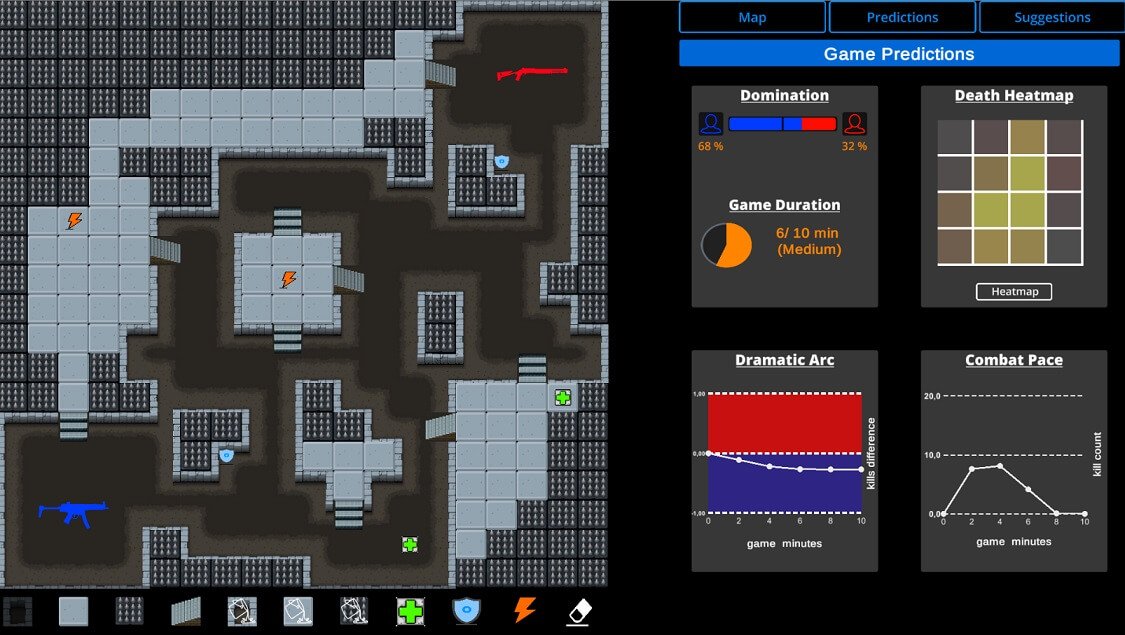
SuSketch drawing interface: the designer draws their desired level via the canvas and tile palette (left half) and the computer predicts a number of gameplay outcomes (aggregated, spatial, or temporal) and visualizes them back to the designer (right half)
Abstract: This paper introduces SuSketch, a design tool for first person shooter levels. SuSketch provides the designer with gameplay predictions for two competing players of specific character classes. The interface allows the designer to work side-by-side with an artificially intelligent creator and to receive varied types of feedback such as path information, predicted balance between players in a complete playthrough, or a predicted heatmap of the locations of player deaths. The system also proactively designs alternatives to the level and class pairing, and presents them to the designer as suggestions that improve the predicted balance of the game. SuSketch offers a new way of integrating machine learning into mixed-initiative co-creation tools, as a surrogate of human play trained on a large corpus of artificial playtraces. A user study with 16 game developers indicated that the tool was easy to use, but also highlighted a need to make SuSketch more accessible and more explainable.
in IEEE Transactions on Games 14(2), pp. 273-283. 2021. BibTex
Djehuty: A Mixed-Initiative Handwriting Game for Preschoolers
Jean Michel A. Sarr, Georgios N. Yannakakis, Antonios Liapis, Alassane Bah and Christophe Cambier
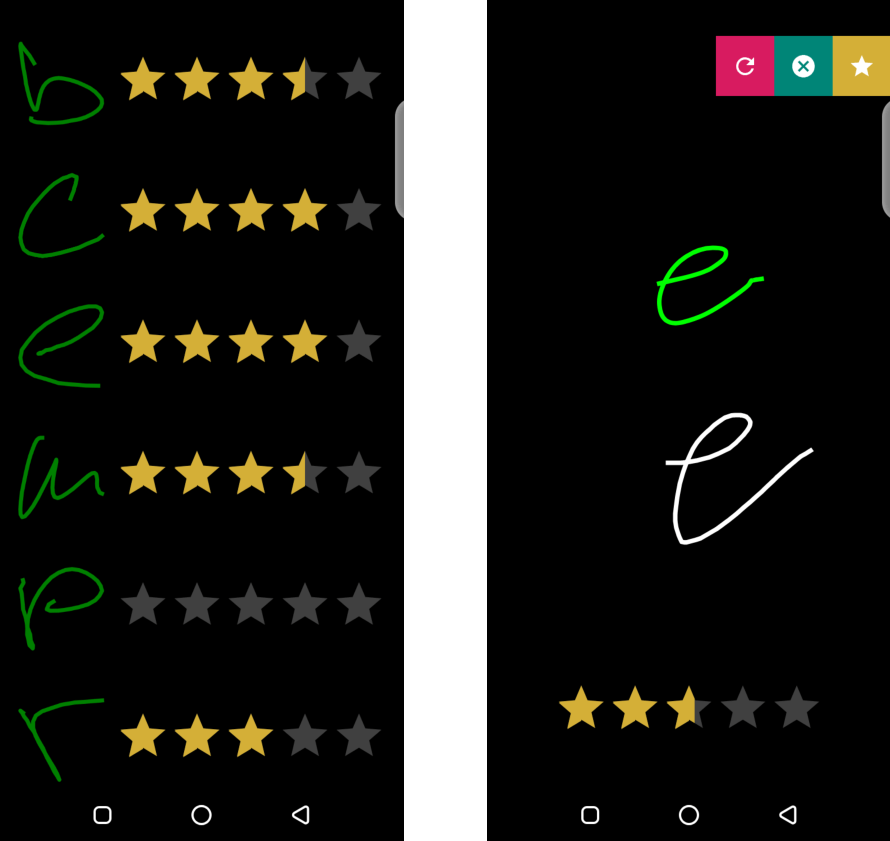
Screenshots of learners' interaction with Djehuty. Left: letter selection, showing the learner's highest score per letter. Right: the computer generates and animates a letter sample (in green), the user draws (in white) and presses the yellow "star" button to receive a score in real-time.
Abstract: Learning to read and write is a fundamental right and a necessary skill for the personal, cultural, and economic development of people and their societies. However, children of developing countries, such as sub-Saharan areas, are currently at a greater risk of illiteracy. The current penetration of mobile technologies and the internet in sub-Saharan rural areas, however, offers a unique opportunity for tackling the challenge of literacy at a large scale. Motivated by the current shortage of preschool teachers for training handwriting in a personalised manner, this paper discusses the design of Djehuty, an educational gamified environment for preschoolers. Djehuty is equipped with an artificial intelligence module which generates a style of handwriting and suggests handwriting paths to the child in a mixed-initiative manner. The paper presents the key elements of the game prototype.
in Proceedings of the Foundations of Digital Games Conference, 2020. BibTex
Explainable AI for Designers: A Human-Centered Perspective on Mixed-Initiative Co-Creation
Jichen Zhu, Antonios Liapis, Sebastian Risi, Rafael Bidarra and G. Michael Youngblood
Abstract: Growing interest in eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) aims to make AI and machine learning more understandable to human users. However, most existing work focuses on new algorithms, and not on usability, practical interpretability and efficacy on real users. In this vision paper, we propose a new research area of eXplainable AI for Designers (XAID), specifically for game designers. By focusing on a specific user group, their needs and tasks, we propose a human-centered approach for facilitating game designers to co-create with AI/ML techniques through XAID. We illustrate our initial XAID framework through three use cases, which require an understanding both of the innate properties of the AI techniques and users' needs, and we identify key open challenges.
in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence and Games, 2018. BibTex
Mixed-Initiative Creative Interfaces
Sebastian Deterding, Jonathan Hook, Rebecca fiebrink, Marco Gillies, Jeremy Gow, Memo Akten, Gillian Smith, Antonios Liapis and Kate Compton

The spectrum of agency and initiative distribution in creative interfaces.
Abstract: Enabled by artificial intelligence techniques, we are witnessing the rise of a new paradigm of computational creativity support: mixed-initiative creative interfaces put human and computer in a tight interactive loop where each suggests, produces, evaluates, modifies, and selects creative outputs in response to the other. This paradigm could broaden and amplify creative capacity for all, but has so far remained mostly confined to artificial intelligence for game content generation, and faces many unsolved interaction design challenges. This workshop therefore convenes CHI and game researchers to advance mixed-initiative approaches to creativity support.
In Proceedings of the CHI Conference Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 2017. BibTex
Mixed-initiative Creative Drawing with webIconoscope
Antonios Liapis
Example icons created by webIconoscope, seen through the voting gallery which allows users to guess which concept (of three) each icon represents, as well as rate its general appeal.
Abstract: This paper presents the webIcononscope tool for creative drawing, which allows users to draw simple icons composed of basic shapes and colors in order to represent abstract semantic concepts. The goal of this creative exercise is to create icons that are ambiguous enough to confuse other people attempting to guess which concept they represent. webIcononscope is available online and all creations can be browsed, rated and voted on by anyone; this democratizes the creative process and increases the motivation for creating both appealing and ambiguous icons. To complement the creativity of the human users attempting to create novel icons, several computational assistants provide suggestions which alter what the user is currently drawing based on certain criteria such as typicality and novelty. This paper reports trends in the creations of webIcononscope users, based also on feedback from an online audience.
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computational Intelligence in Music, Sound, Art and Design (EvoMusArt), vol. 10198, LNCS. Springer, 2017. BibTex
Mixed-initiative Content Creation
Antonios Liapis, Gillian Smith and Noor Shaker
Abstract: Algorithms can generate game content, but so can humans. And while PCG algorithms can generate some kinds of game content remarkably well and extremely quickly, some other types (and aspects) of game content are still best made by humans. Can we combine the advantages of procedural generation and human creation somehow? This chapter discusses mixed-initiative systems for PCG, where both humans and software have agency and co-create content. A small taxonomy is presented of different ways in which humans and algorithms can collaborate, and then three mixed-initiative PCG systems are discussed in some detail: Tanagra, Sentient Sketchbook, and Ropossum.
In Procedural Content Generation in Games: A Textbook and an Overview of Current Research, Noor Shaker, Julian Togelius and Mark J. Nelson (Eds.). Springer, 2016. BibTex
Can Computers Foster Human Users' Creativity? Theory and Praxis of Mixed-Initiative Co-Creativity
Antonios Liapis, Georgios N. Yannakakis, Constantine Alexopoulos and Phil Lopes

An overview of the ideal flow of collaborative mixed-initiative co-creativity. Elements of this ideal flow are implemented and tested in prototypes described in the article.
Abstract: This article discusses the impact of artificially intelligent computers to the process of design, play and educational activities. A computational process which has the necessary intelligence and creativity to take a proactive role in such activities can not only support human creativity but also foster it and prompt lateral thinking. The argument is made both from the perspective of human creativity, where the computational input is treated as an external stimulus which triggers re-framing of humans' routines and mental associations, but also from the perspective of computational creativity where human input and initiative constrains the search space of the algorithm, enabling it to focus on specific possible solutions to a problem rather than globally search for the optimal. The article reviews four mixed-initiative tools (for design and educational play) based on how they contribute to human-machine co-creativity. These paradigms serve different purposes, afford different human interaction methods and incorporate different computationally creative processes. Assessing how co-creativity is facilitated on a per-paradigm basis strengthens the theoretical argument and provides an initial seed for future work in the burgeoning domain of mixed-initiative interaction.
Digital Culture & Education (DCE), 8 (2). 2016. BibTex
Boosting Computational Creativity with Human Interaction in Mixed-Initiative Co-Creation Tasks
Antonios Liapis and Georgios N. Yannakakis
The spectrum between human-led and computer-led creativity, and the mixed-initiative design tools examined in this paper.
Abstract: Research in computational creativity often focuses on autonomously creative systems, which incorporate creative processes and result in creative outcomes. However, the integration of artificially intelligent processes in human-computer interaction tools necessitates that we identify how computational creativity can be shaped and ultimately enhanced by human intervention. This paper attempts to connect mixed-initiative design with established theories of computational creativity, and adapt the latter to accommodate a human initiative impacting computationally creative processes and outcomes. Several case studies of mixed-initiative tools for design and play are used to corroborate the arguments in this paper.
in Proceedings of the ICCC workshop on Computational Creativity and Games. 2016. BibTex
A Constructive Approach for the Generation of Underwater Environments
Ryan Abela, Antonios Liapis and Georgios N. Yannakakis

Marine sessile organisms generated by the Coralize tool: hard corals (left), soft corals (top right) and sponges (bottom right).
Abstract: This paper introduces Coralize, a library of generators for marine organisms such as corals and sponges. Using constructive algorithms, Coralize can generate stony corals via L-system grammars, soft corals via leaf venation algorithms and sponges via nutrient-based mesh growth. The generative algorithms are parameterizable, allowing a user to adjust the parameters in order to create visually appealing 3D meshes. Such meshes can be used to automatically populate a seabed or reef, in order to create a biologically realistic and aesthetically pleasing underwater environment.
in Proceedings of the FDG workshop on Procedural Content Generation in Games, 2015. BibTex
Motivating Visual Interpretations in Iconoscope: Designing a Game for Fostering Creativity
Antonios Liapis, Amy K. Hoover, Georgios N. Yannakakis, Constantine Alexopoulos and Evangelia V. Dimaraki
The drawing interface of Iconoscope, where a user creates an icon with colorful shapes to represent a word-concept shown at the top left corner.
Abstract: This paper introduces Iconoscope, a game aiming to foster the creativity of a young target audience in formal or informal educational settings. At the core of the Iconoscope design is the creative, playful interpretation of word-concepts via the construction of visual icons. In addition to that, then game rewards ambiguity via a scoring system which favors icons that dichotomize public opinion. The game is played by a group of players, with each player attempting to guess which of the concepts provided by the system is represented by each opponent's created icon. Through the social interaction that emerges, Iconoscope prompts co-creativity within a group of players; in addition, the game offers the potential of human-machine co-creativity via computer-generated suggestions to the player's icon. Experiments with early prototypes, described in this paper, provide insight into the design process and motivate certain decisions taken for the current version of Iconoscope which, at the time of writing, is being evaluated in selected schools in Greece, Austria and the United Kingdom.
in Proceedings of the 10th Conference on the Foundations of Digital Games, 2015. BibTex
DrawCompileEvolve: Sparking Interactive Evolutionary Art with Human Creations
Jinhong Zhang, Rasmus Taarnby, Antonios Liapis and Sebastian Risi
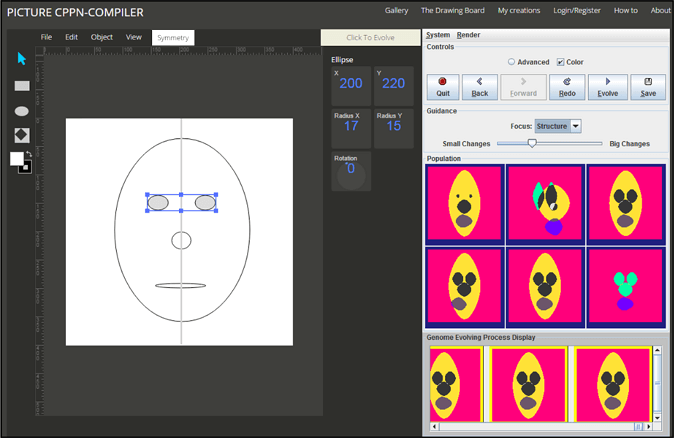
Using the interface of DrawCompileEvolve, the user can draw a SVG image on the canvas (left) and can compile and evolve it as a CPPN image (right) via the Picbreeder applet.
Abstract: This paper presents DrawCompileEvolve, a web-based drawing tool which allows users to draw simple primitive shapes, group them together or define patterns in their groupings (e.g. symmetry, repetition). The user's vector drawing is then compiled into an indirectly encoded genetic representation, which can then be evolved interactively, allowing the user to change the image's colors, patterns and ultimately transform it. The human artist has direct control while drawing the initial seed of an evolutionary run and indirect control while interactively evolving it, thus making DrawCompileEvolve a mixed-initiative art tool. Early results in this paper show the potential of DrawCompileEvolve to jump-start evolutionary art with meaningful drawings as well as the power of the underlying genetic representation to transform the user's initial drawing into a different, yet potentially meaningful, artistic rendering.
in Evolutionary and Biologically Inspired Music, Sound, Art and Design (EvoMusArt), vol. 9027, LNCS. Springer, 2015. BibTex
Designer Modeling for Sentient Sketchbook
Antonios Liapis, Georgios N. Yannakakis and Julian Togelius
Adapting the suggestions of Sentient Sketchbook to match the detected designer goals of rotational symmetry.
Abstract: This paper documents the challenges in creating a computer-aided level design tool which incorporates computer-generated suggestions which appeal to the human user. Several steps are suggested in order to make the suggestions more appropriate to a specific user's overall style, current focus, and end-goals. Designer style is modeled via choice-based interactive evolution which adapts the impact of different dimensions of quality based on the designer's choice of certain suggestions over others. Modeling process is carried out similarly to style, but adapting to the current focus of the designer's actions. Goals are modeled by estimating the visual patterns of the designer's final artifact and changing the parameters of the algorithm to enforce such patterns on generated suggestions.
in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence and Games (CIG), 2014. BibTex
The Case for a Mixed-Initiative Collaborative Neuroevolution Approach
Sebastian Risi, Jinhong Zhang, Rasmus Taarnby, Peter Greve, Jan Piskur, Antonios Liapis and Julian Togelius
Abstract: It is clear that the current attempts at using algorithms to create artificial neural networks have had mixed success at best when it comes to creating large networks and/or complex behavior. This should not be unexpected, as creating an artificial brain is essentially a design problem. Human design ingenuity still surpasses computational design for most tasks in most domains, including architecture, game design, and authoring literary fiction. This leads us to ask which the best way is to combine human and machine design capacities when it comes to designing artificial brains. Both of them have their strengths and weaknesses; for example, humans are much too slow to manually specify thousands of neurons, let alone the billions of neurons that go into a human brain, but on the other hand they can rely on a vast repository of common-sense understanding and design heuristics that can help them perform a much better guided search in design space than an algorithm. Therefore, in this paper we argue for a mixed-initiative approach for collaborative online brain building and present first results towards this goal.
in Proceedings of the ALIFE workshop on Artificial Life and the Web, 2014. BibTex
Mixed-Initiative Co-Creativity
Georgios N. Yannakakis, Antonios Liapis and Constantine Alexopoulos
Step-by-step design sessions of Sentient Sketchbook users, with computational suggestions as red arrows and creative milestones as circles.
Abstract: Creating and designing with a machine: do we merely create together (co-create) or can a machine truly foster our creativity as human creators? When does such co-creation foster the co-creativity of both humans and machines? This paper investigates the simultaneous and/or iterative process of human and computational creators in a mixed-initiative fashion within the context of game design and attempts to draw from both theory and praxis towards answering the above questions. For this purpose, we first discuss the strong links between mixed-initiative co-creation and theories of human and computational creativity. We then introduce an assessment methodology of mixed-initiative co-creativity and, as a proof of concept, evaluate Sentient Sketchbook as a co-creation tool for game design. Core findings suggest that tools such as Sentient Sketchbook are not mere game authoring systems or mere enablers of creation but, instead, foster human creativity and realize mixed-initiative co-creativity.
in Proceedings of the 9th Conference on the Foundations of Digital Games, 2014. BibTex
Designer Modeling for Personalized Game Content Creation Tools
Antonios Liapis, Georgios N. Yannakakis and Julian Togelius

The designer model incorporated in a computer-aided design (CAD) process.
Abstract: With the growing use of automated content creation and computer-aided design tools in game development, there is potential for enhancing the design process through personalized interactions between the software and the game developer. This paper proposes designer modeling for capturing the designer's preferences, goals and processes from their interaction with a computer-aided design tool, and suggests methods and domains within game development where such a model can be applied. We describe how designer modeling could be integrated with current work on automated and mixed-initiative content creation, and envision future directions which focus on personalizing the processes to a designer's particular wishes.
in Proceedings of the AIIDE Workshop on Artificial Intelligence & Game Aesthetics, 2013. BibTex
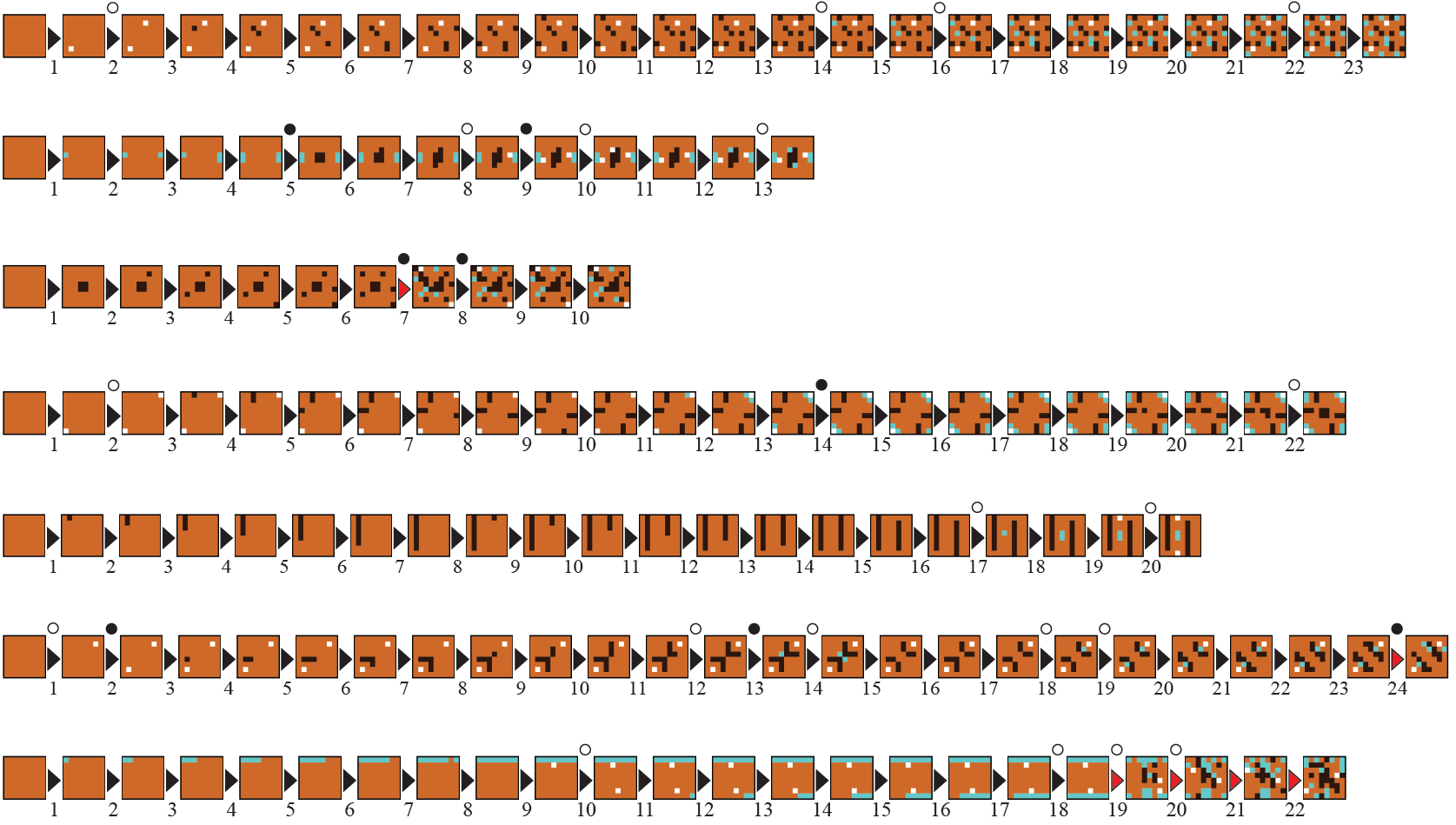
Adaptive Game Level Creation through Rank-based Interactive Evolution
Antonios Liapis, Hector P. Martinez, Julian Togelius and Georgios N. Yannakakis
User interface for ranking maps according to preference. Rank-based interactive evolution is then applied to create new, personalized content.
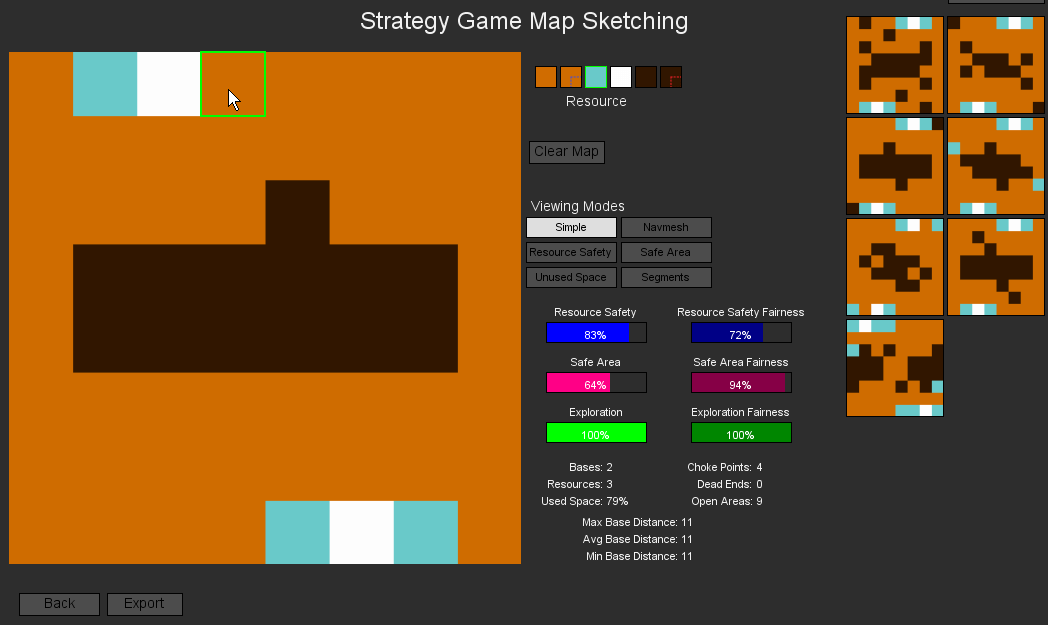
Abstract: This paper introduces Rank-based Interactive Evolution (RIE) which is an alternative to interactive evolution driven by computational models of user preferences to generate personalized content. In RIE, the computational models are adapted to the preferences of users which, in turn, are used as fitness functions for the optimization of the generated content. The preference models are built via ranking-based preference learning, while the content is generated via evolutionary search. The proposed method is evaluated on the creation of strategy game maps, and its performance is tested using artificial agents. Results suggest that RIE is both faster and more robust than standard interactive evolution and outperforms other state-of-the-art interactive evolution approaches.
in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence and Games (CIG), 2013. BibTex
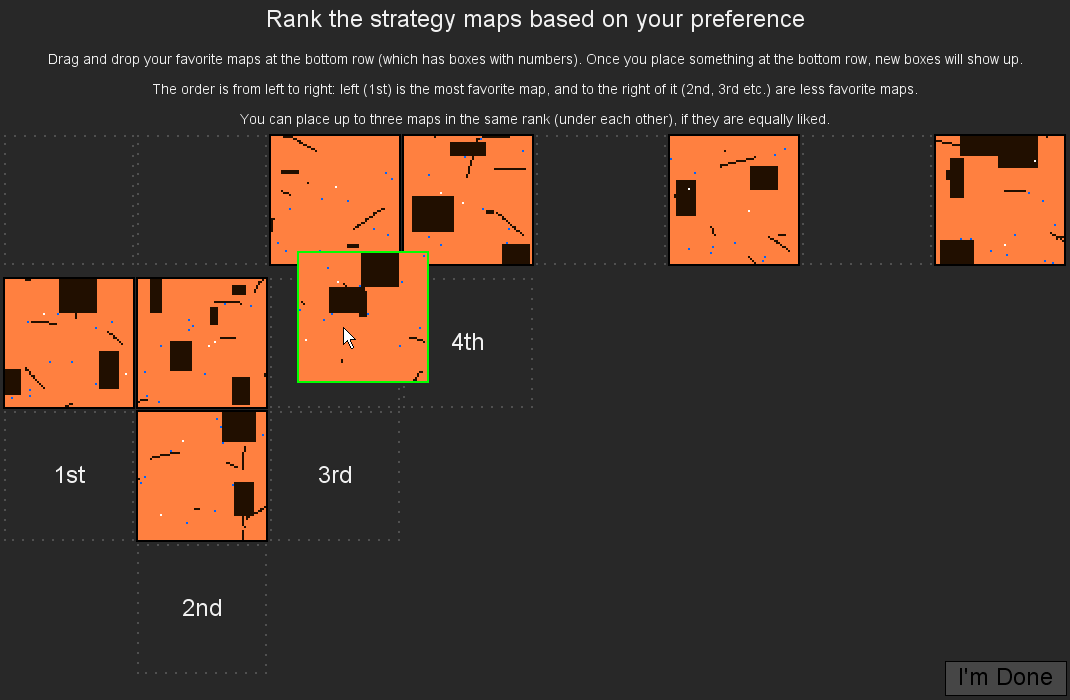
Sentient Sketchbook: Computer-Aided Game Level Authoring
Antonios Liapis, Georgios N. Yannakakis and Julian Togelius
User interface of Sentient Sketchbook, with the user working on the map sketch canvas (left) and the computer generating suggestions in real-time (far right).
Abstract: This paper introduces the Sentient Sketchbook, a tool which supports a designer in the creation of game levels. Using map sketches to alleviate designer effort, the tool automates playability checks and evaluations and visualizes significant gameplay properties. This paper also introduces constrained novelty search via a two-population paradigm for generating, in real-time, alternatives to the author's design and evaluates its potential against current approaches. The paper concludes with a small-scale user study in which industry experts interact with the Sentient Sketchbook to design game levels. Results demonstrate the tool's potential and provide directions for its improvement.
in Proceedings of the 8th Conference on the Foundations of Digital Games, 2013, pp. 213-220. BibTex
Sentient World: Human-Based Procedural Cartography
Antonios Liapis, Georgios N. Yannakakis and Julian Togelius
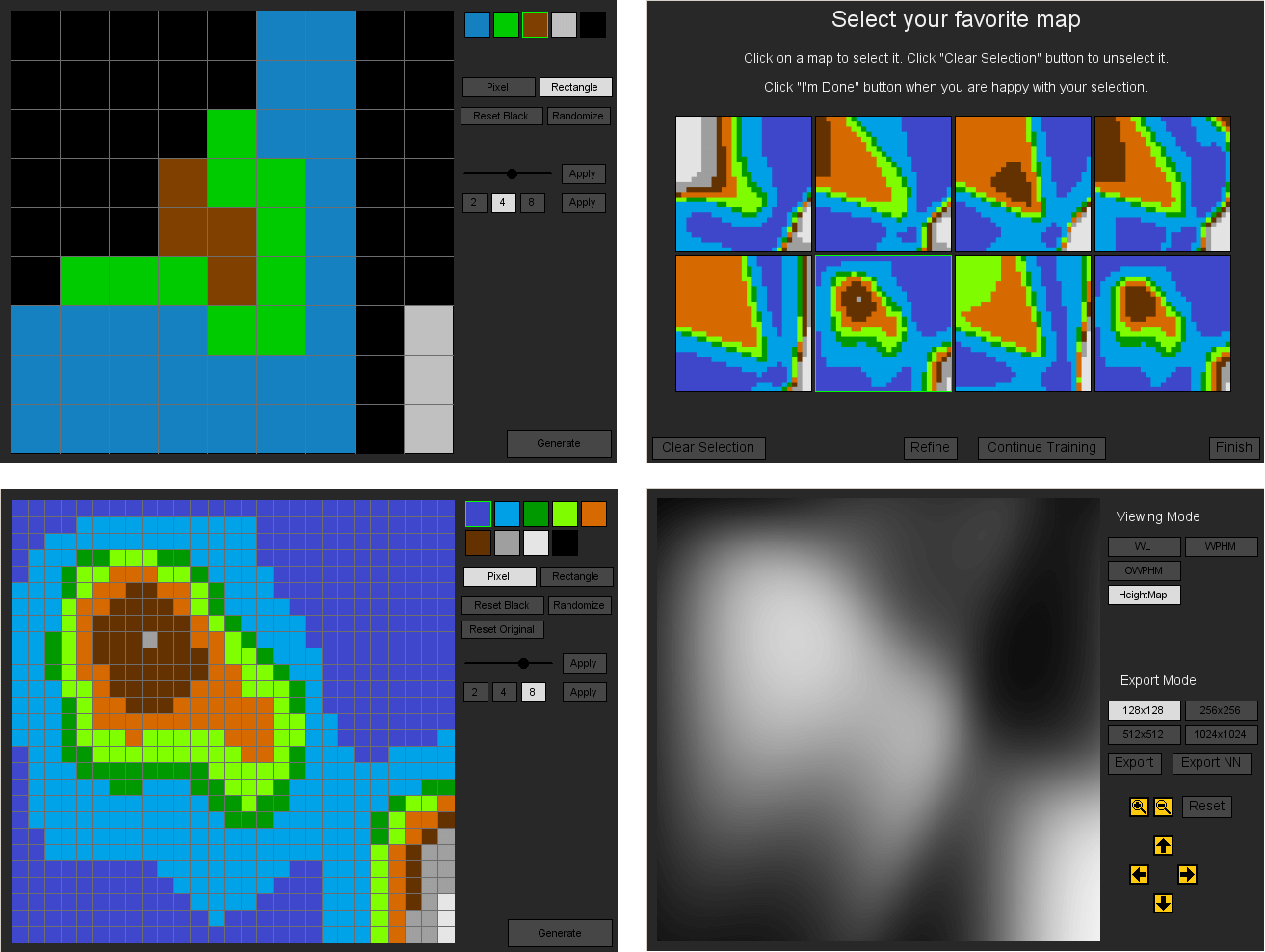
Different steps of the design process of terrain using Sentient World: the user draws a rough terrain sketch using coarse height brushes (top left), which Sentient World refines and shows possible higher-detail maps to the user (top right). The user can manual edit the refined map and submit it for further refinement (bottom left), while the final output is a map of infinite resolution which can be visualized in many different ways (bottom right).
Abstract: This paper presents a first step towards a mixed-initiative tool for the creation of game maps. The tool, named Sentient World, allows the designer to draw a rough terrain sketch, adding extra levels of detail through stochastic and gradient search. Novelty search generates a number of dissimilar artificial neural networks that are trained to approximate a designer's sketch and provide maps of higher resolution back to the designer. As the procedurally generated maps are presented to the designer (to accept, reject, or edit) the terrain sketches are iteratively refined into complete high resolution maps which may diverge from initial designer concepts. The tool supports designer creativity while conforming to designer intentions, and maintains constant designer control through the map selection and map editing options. Results obtained on a number of test maps show that novelty search is beneficial for introducing divergent content to the designer without reducing the speed of iterative map refinement.
in Proceedings of Evolutionary and Biologically Inspired Music, Sound, Art and Design (EvoMusArt), vol. 7834, LNCS. Springer, 2013, pp. 180-191. BibTex
Limitations of Choice-Based Interactive Evolution for Game Level Design
Antonios Liapis, Georgios N. Yannakakis and Julian Togelius
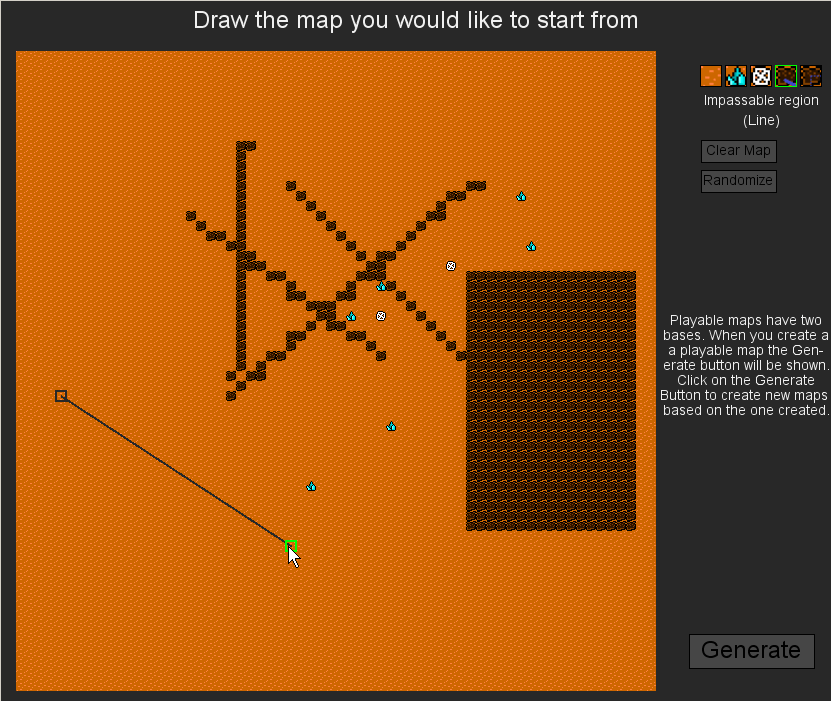
Map editor while a new map is created by the user to seed evolution.
Abstract: This paper presents a tool geared towards the collaboration of a human and an artificial designer for the creation of game content. The framework combines procedural content generation using stochastic search with user input in the form of an initial goal statement as well as preference of generated results. Feedback from industry experts in a pilot user experiment showcased the limitations of this approach and the protocol chosen for evaluating the authoring tool. The limitations are discussed with respect to the suitability of interactive evolution for creative design and the design of experimental protocols for evaluating authoring tools for games.
in Proceedings of the AIIDE Workshop on Human Computation in Digital Entertainment, 2012. BibTex